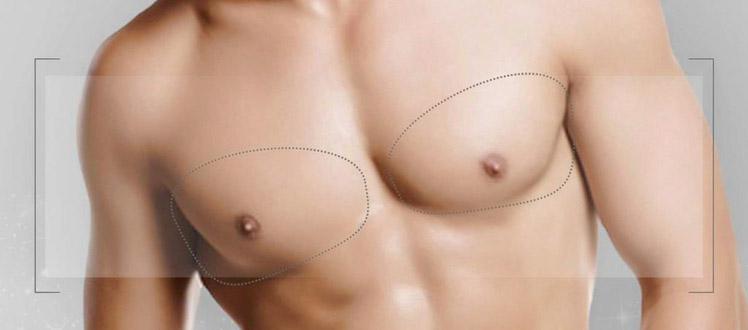
Hypertrophied male breast is actually a very common condition, with around 50% of men affected to varying degrees. Usually linked to gynecomastia, which is the overgrowth of male mammary glands. When this condition occurs, it often comes with confidence and body image issues. What causes gynecomastia ? How is this condition treated ? Here are the answers to these questions.
Hypertrophied male breasts : what’s the cause ? How is it treated ?
Gynecomastia : causes
Gynecomastia is often linked to the patient’s physiognomy
80% to 90% of newborns present with gynecomastia which has developed under the influence of estrogen transferred from the placenta to the blood stream. In this case, gynecomastia resolves very early on during the child’s growth. At puberty, hormonal imbalances are common and can translate to a mild gynecomastia. In this case, the condition usually resolves by itself overtime, but it can persist. Less often, men in their fifties can develop gynecomastia, which is linked to age related androgen decrease.
Endocrinal conditions
Gynecomastia is sometimes linked to an endocrinal gland disorder. This genetic defect assigns to a male individual an additional X chromosome, which is why testosterone production is too low or non existent and male attributes have difficulties developing, which female characteristics appearing during puberty.
Treating gynecomastia
Surgical treatment can remove excess fat as well as glandular tissue to restore normal proportions in the male torso. In mild to moderate cases, standalone liposuction can be used to treat gynecomastia. Short incisions (2 to 3 mm) in each side of the thorax allow access to fat deposits. In pronounced cases, if there is an overgrowth of glandular tissue, direct removal has to be combined with liposuction. This techniques uses an incision in the lower part of the areola to allow access to excess tissues. In severe cases, the breast reduction technique is usually required to restore normal proportions.